GASEOUS EXCHANGE biology class 10 notes Chapter No 10
Shams Notes biology class 10 chapter 10 notes kips academy and all kpk educational Board. class 10 biology chapter 10 GASEOUS EXCHANGE short questions. gaseous exchange in human class 10 biology notes pdf.
Answer the following question
Q1: Write a short note on the Gaseous exchange, respiration, photosynthesis, and breathing?
Ans: Gaseous exchange:
The diffusion of gases like oxygen and carbon dioxide between organisms and their environment is called a gaseous exchange.
Gaseous exchange occurs from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration. It occurs both in plants and animals.
- In animals, gaseous exchange occurs through lungs and gills.
- In plants, gaseous exchange takes place through the general body surface mainly through stomata of leaves and young stems.
Photosynthesis:
The process in which green plants prepare their food (glucose) from carbon dioxide (CO2) and water (H20) using the energy of sunlight is called Photosynthesis.
Photosynthesis occurs in green parts of plants such as leaves and young stems. These parts contain chlorophyll (green pigment) which is necessary for photosynthesis. Sun is the main source of energy for photosynthesis. Photosynthesis is a constructive process in which glucose molecules are formed.
Respiration:
The process in which glucose molecules are broken down to release energy is called respiration.
Respiration takes place in both animals and plants. In this process energy (ATP) is produced according to the need of organisms. The organisms use this energy for their vital activities. Respiration is a destructive process in which glucose molecules are broken down.
Breathing:
The process of inhalation and exhalation for the intake of oxygen (02) and giving out of carbon dioxide (CO2) is called breathing.
Normally breathing is an involuntary process and its center is located in the medulla of the brain. The normal rate of breathing is 15-20 times per minute under resting condition.
Q 2: Explain gaseous exchange in plants with mechanisms? Ans: Gaseous exchange:
The diffusion of gases like oxygen and carbon dioxide between organisms and their environment is called a gaseous exchange.
The gaseous exchange in plants occurs between plants' body and their environment. Plants have no specialized organs for gaseous exchange because plants have a large surface area in proportion to their volume. Therefore plants diffuse gases through their general body surface.
Aquatic plants:
Aquatic plants obtain the dissolved oxygen in water by the process of diffusion through their roots.
Terrestrial plants:
Inland plants, gaseous exchange occurs mainly through stomata present in leaves and young stems. Stomata are small pores through which gases and water vapor diffuse.
Woody plants:
In mature woody plants, gaseous exchange occurs through lenticels. Lenticels are scars and crake on a woody stem.
Mechanism:
At night time Plants take oxygen from the environment through stomata. After entering into plant body oxygen diffuse into intercellular spaces. From there oxygen diffuses into cells and dissolves in the cell sap. Cell sap carries that oxygen to the respiratory center of cells called mitochondria. Respiration occurs in mitochondria which produce energy and release carbon dioxide.
Q: 3 Write a detailed note on gaseous exchange in humans?
Ans: Gaseous exchange:
The diffusion of gases like oxygen (O2) and carbon dioxide (CO2) between organisms and their environment is called gaseous exchange or exchange of gases.
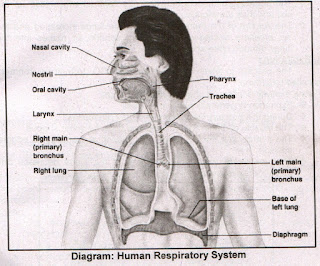
Gaseous exchanges in humans occur between the human body and their environment. Humans have a specialized respiratory system which is well adapted for the terrestrial mode of life. The respiratory systems of humans divided into two main parts.
- Air passageway
- Lungs
- Air passageway:
The Air passageway consists of the following parts.
i. Nose ii. Nasal cavity iii. Pharynx
iv. Larynx v. Trachea vi. Bronchi
i. Nose:
The nose is the externally visible part of the respiratory system. The nose contains two openings called nostrils.
Function:
The nose allows air from the outside environment inside the body.
ii. Nasal cavities:
The nose contains two chambers called Nasal cavities. These chambers are lined by mucous membranes along with hairs. The mucous membrane secretes a sticky substance called mucus.
Function:
- Mucus and hairs filter the air and prevent the entry of dust particles and microorganisms inside the respiratory system.
- Mucus also helps in the moistening of the air and regulates air temperature to the internal body temperature.
iii. Pharynx:
Air from the nasal cavity enters into pharynx through apertures called internal nares. It is about 4.5 inches long muscular passage lined by mucous membrane.
Function:
- It contains tonsils and adenoids which are the organs of lymphatic tissue used to trap and filter microorganisms. It allows air from the nasal cavity to the pharynx.
vi. Larynx (voice box):
The larynx is present on the anterior part of the air tube(trachea). Air passes from pharynx to larynx. In the larynx, a Cavity is presently called glottis which is guarded by a cartilaginous flap called epiglottis.
Function:
- When we inhale air, the epiglottis closes the glottis to prevent the entry of the food or liquid into the larynx.
- Two fibers band called vocal cards are located in the larynx which on vibration produces sound. Therefore larynx is also called a soundbox.
v. Trachea (Windpipe):
The larynx opens into the trachea. It lies ventral to the esophagus and extends to the chest cavity. It is about 12 cm long and 2 cm wide tube.
Function:
The trachea has 16 to 20 C-shaped cartilaginous rings which prevent it from collapsing and keep the passage of air open.
vi. Bronchi:
Inside the thorax, the trachea divides into two branches called bronchi (sing. bronchus). Each bronchus enters the lungs of its own side. Inside the lungs, each bronchus divides and sub-divides into small tubes called bronchioles. Bronchioles carry air into the air sacs.
2. Lungs:
Lungs are the respiratory organs of human beings.
Number: Humans have two lungs, right and left. These are slightly unequal in size. Right lung composed of three lobes while the left lung has only two lobes.
Location: Lungs are located in the chest cavity attached to the sternum (chest bone).
Pleura: Lungs are surrounded by a double layer membrane called pleura. Between the membranes, fluid is present which helps in the contraction and relaxation of the lungs.
Air sac: Lungs contain a large number of air sac which looks like a bunch of grapes. Each air sac consists of many microscopic structures called alveoli. There are 274-790 million alveoli present in the lungs. Each alveolus is surrounded by blood capillaries where the exchange of gases occurs between the blood and alveoli.
Diagram: Human Respiratory System
Q 4: Describe the mechanism of breathing in human beings?
Ans: Breathing:
The inhalation and exhalation of air for the intake of oxygen (O2) and giving out of carbon dioxide (O2) is called breathing. In terrestrial animals breathing process occurs through the lungs.
i. Inspiration
ii. Expiration
i. Inspiration;
The process in which organisms taking air (02) from their environment is called inspiration.
During inspiration following changes occur in the lungs.
- Inspiration is an active process in humans.
- During this process the volume of the thorax increases.
- The muscle of the diaphragm contract so it becomes flattened and lower down the thorax.
- The intercostals muscle between ribs contract which rose up the ribs and thus the thorax.
- The volume of the thorax and that of the lungs increased and the air pressure decreases so the atmospheric air rushes into the lungs through the nose and trachea.
ii. Expiration:
The process in which organisms release CO2 to their environment is called Expiration.
During expiration following changes occur in the lungs,
- Expiration is a generally a passive process.
- During this process, the volume of the thorax decreases.
- The muscle of the diaphragm relaxed and become dome-shaped.
- The intercostals muscle of the ribs relaxed and occupy its original position.
- The volume of the thorax and that of the lungs decrease and pressure is exerted on the lungs to expel air (CO2) out.
Q 5: Discuss gas exchange in the lungs?
Ans: Gaseous exchange in lungs:
Gaseous exchange in the lungs takes place between alveoli and blood capillaries. Alveoli are the basic structural and functional unit of the lungs
Which are surrounded by blood capillaries. Blood capillaries are so small that blood can pass through them in a single file. The walls of alveoli and blood capillaries are thin which provides a site for gaseous exchange.
- When the concentration of oxygen is low in blood capillaries than the alveoli. Therefore, oxygen from alveoli diffuses into blood capillaries making the blood oxygenated.
- Similarly when the CO2 concentration in blood capillaries is greater than the alveoli. Therefore, CO2 diffuses out of the blood into the alveoli and is finally expelled out of the body by expiration.
Q 6: Discuss the biological consequences of smoking.
Ans: Biological consequences of smoking:
Smoking has many negative biological effects on the human body. Tobacco smoke contains tar, nicotine, carbon monoxide, nitrogen oxide, hydrogen cyanide, and metals. The negative impacts of smoking are discussed below.
i. Tar:
- Tar is a brown color sticky substance that destroys the cells of the respiratory surface.
- Tar is the major component of cigarette smoke.
- It is carcinogenic and tumors initiators.
- It stains the finger and teeth of the smoker.
- It also stains the lungs of smokers.
- It produces sputum and mucus.
ii. Nicotine:
- Nicotine increases heart rate, blood pressure, and cause the constriction of blood vessels.
- Nicotine can also increase platelet stickiness in the blood which can cause the blockage of coronary vessels.
- Also, damage muscle and hormonal system.
Full Notes Visit Now: Chapter 10 Biology Class 10 Notes


5 Comments
This comment has been removed by the author.
ReplyDeleteHello Students , for reference you can visit Class 10th Science
ReplyDeleteGreat article,
ReplyDeletetop engineering universities in Pakistan
Thank you for your excellent article. I was taken aback when I came across your webpage.
ReplyDeleteBest Schools in Lahore
Ilmi News
Best Schools in Islamabad
AIOU Tutor 2022
Best Schools in Faisalabad
Good details
ReplyDeletePost a Comment